POWERING DATA-DRIVEN SAFETY.
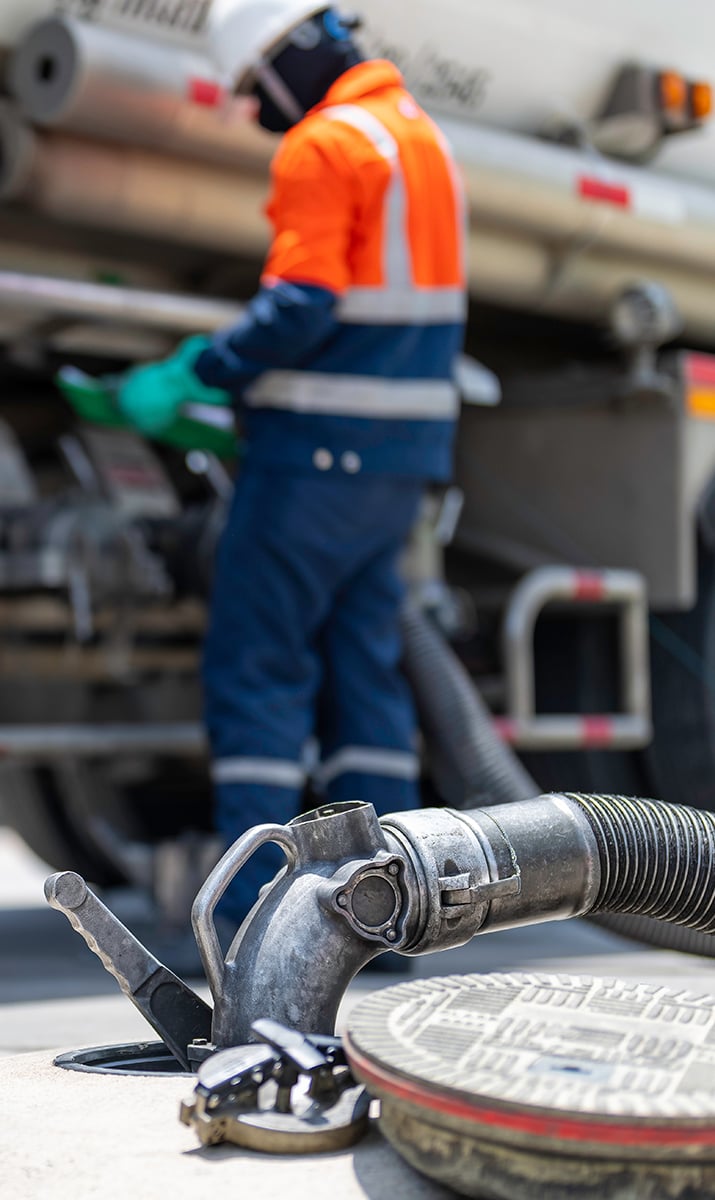
Transportation, logistics and hauling are crucial components in maintaining the supply chain for other industries. Goods and materials need a timely and reliable delivery method which requires dedicated workers to ensure that happens.
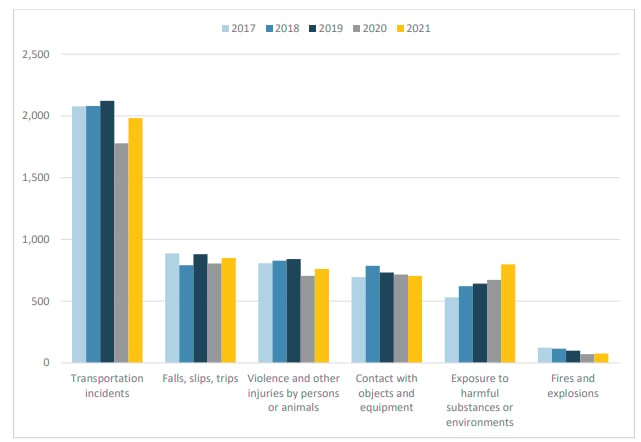
The most common modes of industrial transportation pose a risk to worker safety, from lone worker hazards to potential exposures to gases. Here is a quick look at some of the gas hazards by mode of transportation:
1. Road Transportation - this includes cars, trucks, buses, and other vehicles. It's a convenient and flexible way to move goods over shorter distances. Common gas hazards are carbon monoxide (CO) and flammable liquids and gases such as gasoline, propane, and methane.
2. Rail Transportation - moves heavy goods and materials over long distances. It's efficient and cost-effective, often used for bulk commodities such as coal and grain but also for the transportation of hazardous chemicals such as chlorine (Cl2), ammonia (NH3) and sulfur dioxide (SO2). Trains also frequently transport flammable materials like ethanol, crude oil and natural gas. Many of the types of cargo shipped by trains can be extremely hazardous in the event of a derailment or accident.
3. Air Transportation - moves high-value, time-sensitive goods over long distances. This method is fast but more expensive. Common gas exposures are carbon dioxide (CO2) and combustible gases such as jet fuel vapors.
4. Water Transportation - this includes shipping via container ships, tankers and carriers and reefers. It's an efficient and cost-effective mode of transportation for bulk goods and materials over long distances. Flammable liquids and gases along with carbon monoxide (CO) can pose a risk to workers, as can other harmful gases in confined spaces on marine vessels such as cargo, fuel, sewage and ballast tanks.